cdCon talk by Jamie Plower from Fidelity Investments. “DevOps Intelligence: Scaling Governance, Compliance, & Security across an enterprise of 15K developers”
“continuous compliance” They have a portfolio of components that folks can mix and match for building out a compliant pipeline.
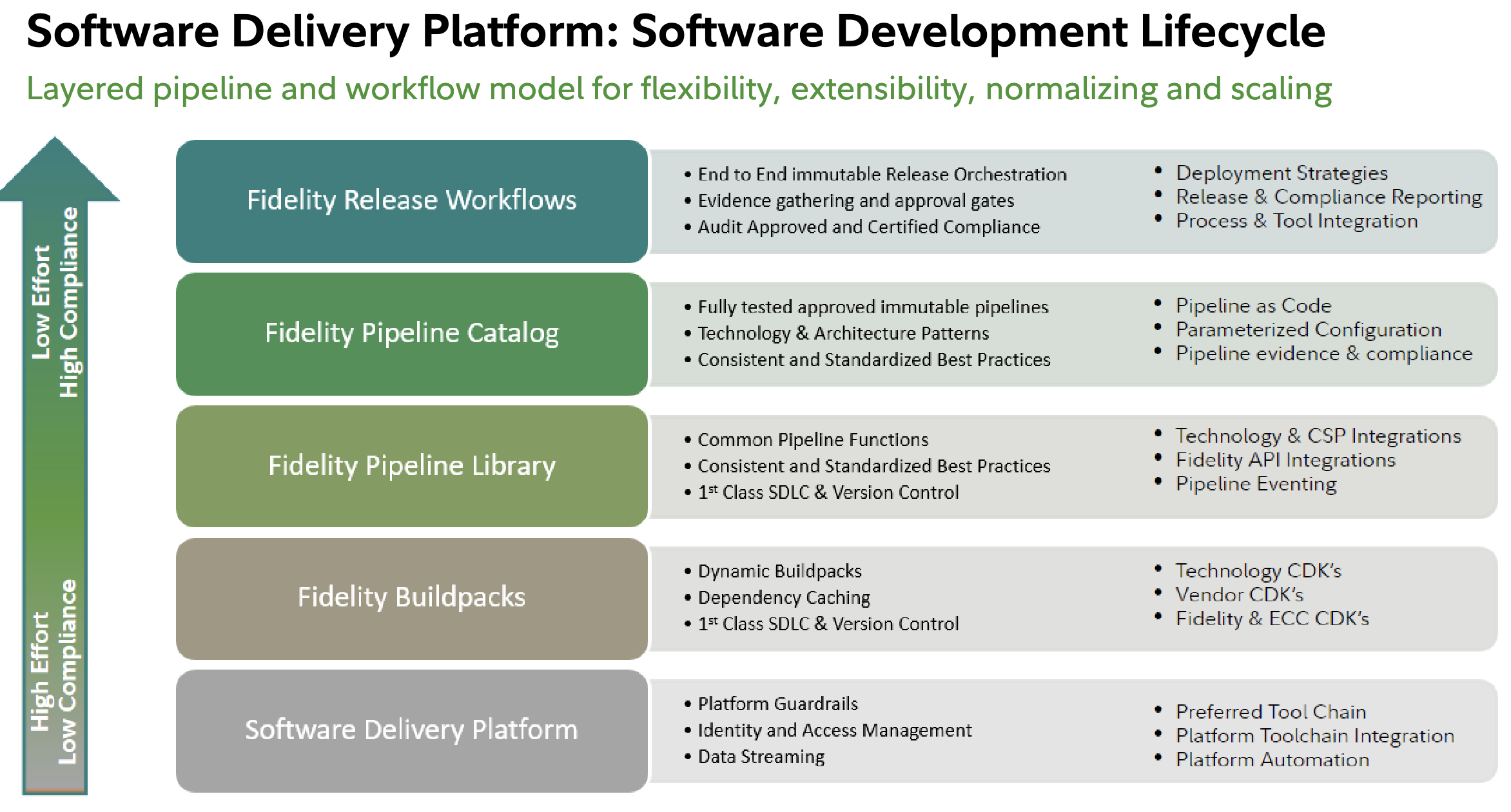
“Policy as code” is a default component of their stack.
They built:
- innersource first
- rewrite internal tools to learn from past mistakes
- built for flexibility. core principe: “enable teams to follow a standard certified pipeline, but let them compose bespoke workflows using catalog segments”
- “devops council” got alignment w/ senior BU stakeholdres
They had a large number of workloads (web services, event driven apps, batch, virtual desktops, etc) that they needed to align.
They broke down their pipeline into individual components (e.g. “sonar scan”). Then they instrumented each of these w/ logs and telemetry. Allowed them to get an understanding of who is using what, get visibility into the KPIs of the pipelines, and funneled information back to the engineering teams responsible for those components.
so pipeline uses components. Components send events into their “intellgence hub” which is the telemetry thing from above.
ITSM - it service management
Their pipeline is able to track things from git sha to build id to artifact id. Basically commit through production.
“In our competitive environment, we can’t afford to have multiple people build it wrong.” - Expressing the importance of inner sourcing and having folks help build a more blessed thing, rather then everyone inventing their own.
Questions:
- curious about the devops council.
- C-level management & developers
Check: Do we follow these controls/standards?
- DONE Completed: 2023-08-15
This has lots of implications for the Supply Chain Security work, specificially the policy portions.
1: SOURCE CODE 2: BUILD 3: SECURITY ANALYSIS 4: TEST 5: PRODUCTION
1.1 “Everything as code” and managed in approved Source Code Control system 1.2 Every change in code is peer reviewed 1.3 All code is free of hard coded credentials and secrets 2.1 Code is built and packaged on approved platform using approved tools and configurations 2.2 Static code analysis is performed, and the code meets preset quality gates 2.3 Unit tests are executed and passed with preset coverage threshold. 2.4 Artifacts produced by the build must be immutable 3.1 Static Application Security Testing performed; results meet security standards 3.2 Software Composition Analysis performed; results meet security standards 3.3 Infrastructure code scanned; results meet security standards 3.4 Container images scanned; results meet security standards 4.1 Functional tests are executed and passed 4.2 Performance tests are executed and passed 4.3 Regression tests are executed and passed 4.4 Chaos tests are executed and passed 5.1 Production access check – ensure that no one has persisted write access to any production resources 5.2 Production monitoring check – ensure that application is setup to be actively monitored using approved monitoring tools